LINK-J, in partnership with UC San Diego, will host the Special Symposium on “Recent Advances in Big Data Analytics and Synthetic Biology: Platform Technologies for Biomanufacturing of the Future” with innovations related to human health in mind. The symposium invites academic leaders in this field to discuss the advances in synthetic biology, material chemistry and big data analytics and their implications for biomanufacturing in various sectors. The symposium also asks industry practitioners to shed light on the exciting potential and challenges of biomanufacturing for human health. The panel discussion is meant to offer a snapshot of where we are in the journey of the bioeconomy revolution.
(Situation of the world surrounding bio manufacturing)
Technological innovations in gene synthesis and editing, coupled with the significant cost reduction in genetic analysis and the widespread use of computing power and artificial intelligence, have opened the doors to the 21st century biotechnology and biomanufacturing. Biomanufacturing is expected to revolutionize a wide range of industries from food to materials to therapeutics in the world. Many industrial countries have announced new initiatives to capitalize on the progress in biotechnology to address societal challenges such as sustainability, climate change and supply chain issues, while leading venture capitalists have expanded investments in synthetic biology startups in recent years. Industry analysis suggests that bioengineering could account for more than a third of global output of manufacturing industries before the end of the decade – almost $30 trillion in terms of value.
U.S. President Biden launched a National Biotechnology and Biomanufacturing Initiative in September 2022. The President’s Executive Order calls on Federal departments and agencies to harness biotechnology and biomanufacturing innovation to further societal goals and transform industries related to: (1) climate change solutions, (2) food and agriculture innovation, (3) supply chain resilience, (4) human health, and (5) cross-cutting advances. U.S. departments and agencies will bolster key steps to enable innovation with funding of more than $2 billion in the immediate future.
*Language:English /Partialy Japanese(English-Japanese simultaneous interpretation available)
*English captions are available (you can choose to turn them on or off).
*Please note that LINK-J and UC San Diego are not responsible for any errors or omissions in the captions.
How to use captions: Managing and viewing closed captioning

Date: Thu, Jun 29, 2:30pm - 7:00pm (JST) (6:00pm -7:00pm Networking)
- In-person:Nihonbashi Life Science Building Room 201
- Networking:Nihonbashi Life Science Building 10F Lounge
- Virtual:Zoom Webinar
(Opens an external site)
定員
リアル会場75名
*リアル会場は先着75名様となります。
オンライン会場1000名
Program
| JST | Agenda |
| 2:30-2:45pm | Opening Remarks - Akihiko Soyama, CEO of LINK-J & Albert P. Pisano, Dean of the Jacobs School of Engineering, UC San Diego |
| 2:45-4:00 | Session 1 – Platform Technologies, moderated by Dean Pisano |
| 2:45-3:15 | Presentation - “Engineering Natural Product Biosynthesis via Protein-Protein Interactions” Dr. Michael Burkart, Professor and Chair, Chemistry & Biochemistry, School of Physical Sciences, UC San Diego |
| 3:15-3:45 | Presentation - “Industrial potential of large-scale and precise genome engineering” Dr. Yasunori Aizawa, Associate Professor of Life Science and Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology/CSO & Co-Founder, LOGOMIX |
| 3:45-4:00 | Presentation - “Systems Biology Research Group at UC San Diego – Status and Capabilities” Dr. Bernhard Palsson, Professor of Bioengineering, UC San Diego – (Recorded) |
| 4:00-5:00 | Session 2 – Global Industrial Trends, moderated by Akihiko Soyama |
| 4:00-4:20 | Presentation - “Global Industrial Trends in Biomanufacturing R&D” Mr. Takeshi Yanagimoto, Managing Director & Partner, Boston Consulting Group Tokyo Office |
| 4:20-4:40 | Presentation - “Microbial gene big data for biomanufacturing” Dr. Masahito Hosokawa, bitBiome Inc. CSO / Waseda University Associate Professor |
| 4:40-5:00 | Presentation - “Monozukuri Strategy of Astellas for Biomanufacturing of the New Modalities” Dr. Hideto Yamaguchi, Senior Vice President, Head of Chemical & Biological Technology Labs. Astellas Pharma Inc. |
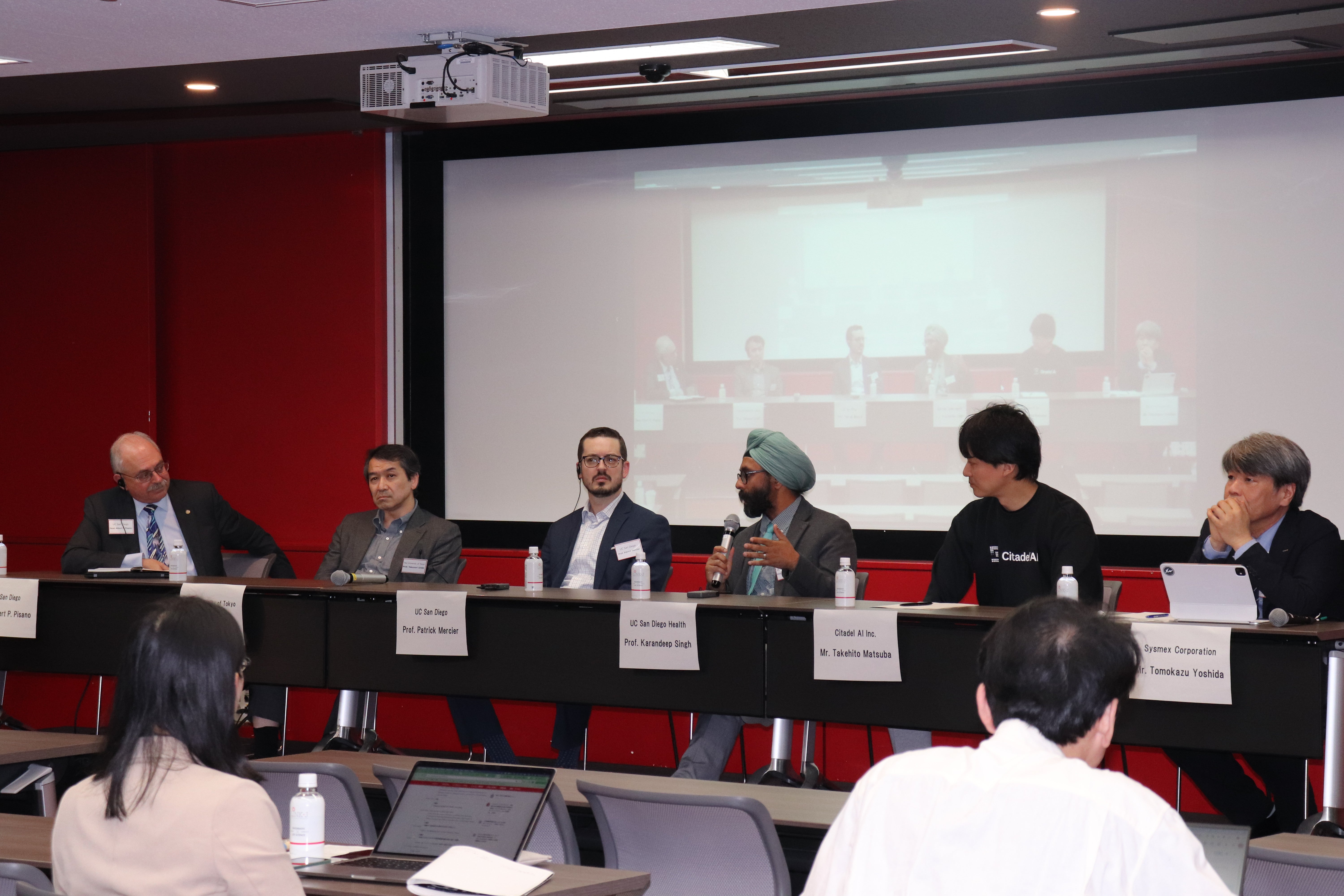
| 5:00-5:40 | Session 3 – Panel Discussion on Biomanufacturing of the Future, moderated by Mr. Yanagimoto Panelists: Dean Pisano Dr. Burkart Dr. Aizawa Dr. Yamaguchi |
| 5:40-5:45 | Closing Remarks - Akihiko Soyama and Miwako Waga (Senior Director of International Outreach, UC San Diego) |
| 6:00-7:00 | Networking Reception |
Speakers
Albert P. Pisano(Dean, Jacobs School of Engineering, UC San Diego)
Michael Burkart(Professor and Chair, Chemistry & Biochemistry, School of Physical Sciences, UC San Diego)
Yasunori Aizawa(Associate Professor of Life Science and Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology/CSO & Co-Founder, LOGOMIX)
Bernhard Palsson(Professor of Bioengineering, UC San Diego)
Takeshi Yanagimoto(Managing Director & Partner, Boston Consulting Group Tokyo Office)
Masahito Hosokawa (bitBiome Inc. CSO / Waseda University Associate Professor)
Hideto Yamaguchi(Senior Vice President, Head of Chemical & Biological Technology Labs. Astellas Pharma Inc.)
Miwako Waga(Senior Director of International Outreach, UC San Diego)
Akihiko Soyama(Chief Executive Officer of LINK-J)
Abstracts
Dr. Aizawa
We find ourselves in a groundbreaking revolution in genomic engineering. Genome sequencing has first provided a wealth of genomic and transcriptomic information across various species and cell types. The resulting knowledge has fueled the development of genome editing, which now extends beyond small indels to encompass megabase-sized changes and has reached the synthesis of complete bacterial and yeast genomes, known as synthetic genomics or genome writing. At my Tokyo Tech lab, we are actively exploring the academic possibilities of genome writing in human cells. Our technology has undergone significant refinement at Logomix Inc., making it suitable for industrial applications. In this presentation, I will introduce our technology and its current applications, with the goal of fostering future collaborations.
Mr. Yanagimoto
This session focuses on the trends and challenges in biopharmaceutical R&D specifically related to biomanufacturing. The first major segment will delve into the current industry R&D trends - how new modalities such as cell & gene therapies, vaccines and recombinant proteins have been evolved in R&D. The session will also commence with an introduction to biomanufacturing, providing an overview of its definition, scope, and its significance in different sectors. The audience will gain insights into the key components and processes involved in biomanufacturing, setting the foundation for the subsequent sessions & discussions.
Dr. Hosokawa
環境破壊や資源枯渇などの社会課題の解決と経済成長を両輪で実現するものとして、「バイオものづくり」が注目されています。日本は発酵・醸造の技術を有しており、化学素材・燃料・食品・医薬品・など多岐にわたる出口があるバイオものづくりで高い競争力を持つと言われます。一方、バイオものづくりの可能性を最大化するには、地球上に膨大に存在する微生物の能力を「ものづくり」に利用できる材料として調達することが開発競争力になります。当社は微生物ゲノムを単一細胞レベルで解析する技術により、「世界最大級の12億遺伝子に上る微生物の遺伝子データ」を保有し、合成生物学・AI・ロボティクス技術を統合し、あらゆる分野のバイオものづくりを強力に支援します。
Dr. Yamaguchi
Astellas has strived to deliver innovative medical solutions that meet patients’ needs. We are committed to achieving our VISION of being “on the forefront of healthcare change, turning innovative science into VALUE for patients.”
We have established a Focus Area Approach for our research and development strategy. Specifically, our Focus Area Strategy is defined as combinations of three components: (1) biologies with high disease relevance, (2) versatile modalities/technologies, and (3) diseases with high unmet medical needs that are expected to be tackled by the first two components. We view this strategy as a way to build a sustainable, expandable drug discovery approach to develop new platforms, leverage expertise and create innovative products. We also focus on the cutting-edge technology such as cell therapy and gene therapy, and work on providing innovative healthcare treatments which can address the root cause of the diseases.
One of the difficult challenges in realizing the Focus Area approach is the early start-up and quality improvement of the new modality manufacturing process.
New modalities, include mRNA drugs such as COVID-19 vaccine, gene therapy using adeno-associated virus, oncolytic virus, autologous cell drugs such as cancer immuno-cell therapy products, and allogeneic cell drugs derived from stem cells, are expected to have high therapeutic potential for diseases for which there were no treatment options until now.
However, biomanufacturing of the new modalities are necessary to overcome difficulties in manufacturing and quality control that are not found in conventional biopharmaceuticals such as small molecules and antibody drugs.
Especially for cell therapy, the manufacturing process takes a relatively longer time period, and in some cases it is not possible to stop the process in the middle, and the definition of drug substance and drug product may become ambiguous. In addition, aseptic filtration cannot be used due to the size of the cells, so sterility must be ensured throughout the manufacturing process. Furthermore, cells are a heterogeneous mixture in terms of quality characteristics such as cell surface expression markers and cell cycle, and also have cell-specific quality characteristics such as genome stability. Therefore, more advanced scientific investigation is required through appropriate specification setting and quality control.
In this presentation, we will summarize the issues in manufacturing and quality control of regenerative medicine products such as viral gene therapy drugs and cell medicines through case studies published by our company and external parties. In order to solve these problems, we will introduce the use of Pharma Capability that we have cultivated so far, and the automation and mechanization of the manufacturing process by introducing so-called Dx technology such as robots and AI.
Capacity
In-person: 75 people
Virtual: 1000 people
Participation Fee
Free
Capacity
リアル会場75名、オンライン1000名
Organizer
Organizer:LINK-J
Co-organizer:University of California San Diego